Which Definition Best Describes a Conduction Block Rhythm
Second Degree Heart Block Type I With second degree heart block Type I some impulses are blocked but not all. Mobitz type I also known as Wenckebach and Mobitz type II12345 NCBI Skip to main.

Identification Of A Scn5a Founder Mutation Causing Sudden Death Brugada Syndrome And Conduction Blocks In Southern Italy Heart Rhythm
Of a poor conduction system.

. HIGH-GRADE OR ADVANCED AV BLOCK. The term block is somewhat misleading in this case because first-degree AV block only implies that the conduction is abnormally slow. AV block represents a delay or disturbance in the transmission of an impulse from the atria to the ventricles.
Symptoms and treatment depend on degree of block but treatment when necessary usually involves pacing. Choose which answer best describes the following rhythm strip. Bundle branch block disruption of impulse conduction from the bundle of His through either the right or left bundle branch to the Purkinje fibers.
However all impulses are conducted to the ventricles. The movement of energy from one. Which of the following best defines conduction.
This system is called the cardiac conduction system. This disruption in normal electrical activity can be transient or permanent and then further characterized as delayed intermittent or absent. True TF The P-P interval is regular with all heart blocks.
The most common cause is idiopathic fibrosis and sclerosis of the conduction system. Conduction block kŏn-dŭkshŭn blok Failure of impulse transmission at some point along a nerve fiber although conduction along the segments proximal and distal to it are unaffected. Of a failure to initiate an impulse.
3 types of conduction blocks defined by their anatomic location. The first-degree heart block takes place where there is an incomplete block. Analysis of first degree heart block is given below and an example is shown in figure 1-22.
Of a block in the conduction system. The ventricles then beat too slowly decreasing the amount of oxygen that gets to the body and brain. Clinically most often the result of an area of focal demyelination or less often transient ischemia.
Three common conduction disorders are. Nonspecific interventricular conduction delay d. Despite the prolonged PR interval every P wave is still followed by a QRS complex - there are no dropped or skipped beats.
The movement of energy by waves that travel through space B. A block in which the sinus node fires normally but the wave of depolarization is immediately blocked and not transmitted to the atrial tissue is which of the following. The movement of a hot liquid of gas from one place to another carrying energy with it C.
AV block may be due to increased vagal tone that may be elicited during sleep athletic training pain or stimulation of the carotid sinus. By definition the PR interval is 022 s. True TF Frequently second degree AV block type I will progress to third degree AV block.
Bundle branch block Explaining the problem. Complete left bundle branch block b. Atrioventricular AV heart block describes impairment of conduction from the atria to the ventricles via the AV junction.
The degree of blockage is dependent on area affected cause of delay or blockage. Diagnosis is by electrocardiography. Your heart rhythm is the way your heart beats.
Conduction is how electrical impulses travel through your heart which causes it to beat. A delay or interruption in impulse conduction from the atria to the ventricles that occurs because of a transient or permanent anatomic or functional impairment describes an AV block. Conduction blocks are classified as either first-degree block second-degree block or third-degree block.
There are two types of second-degree atrioventricular blocks. When the AV conduction ratio is 31 or higher the rhythm is called advanced AV block. AV blocks are conduction delays or a complete block of impulses from the atria into the ventricles.
A conduction disorder also known as heart block is a problem with the electrical system that controls your hearts rate and rhythm. The P-P interval is regular with heart blocks. The signal causes your heart muscle to beat and pump blood to your lungs.
The three commonly described types of AV block are 1st degree 2nd degree and 3rd degree AV block. Heart block rhythms electrical current has difficulty traveling along normal conduction pathway causing a delay in or absence of ventricular depolarization. Medical Dictionary for the Dental Professions Farlex 2012.
You are reviewing an ECG that demonstrates an RSR pattern in lead V1 and the QRS is 013 sec. The second-degree atrioventricular block is the focus of this activity. Some conduction disorders can cause arrhythmias or irregular heartbeats.
Heart blocks are arrhythmias caused by conduction disturbances at the AV node. Identifying the type of second-degree block in such instances is also difficult. Three levels of heart blocks.
In second-degree AVB with 21 conduction the block can be either nodal or infranodal and making this distinction is key to its management. The PR interval in a first-degree heart block is prolonged which means the electrical conduction from the atria to the ventricles is delayed. This means than the PR Interval will be longer than normal over 020 sec.
Atrioventricular AV block is partial or complete interruption of impulse transmission from the atria to the ventricles. First Degree Heart Block. This causes a slow pulse and can result in a lack of energy feeling lightheaded or fainting.
First-Degree Incomplete Heart Block. It is caused by a conduction delay at the AV node or bundle of His. Incomplete left bundle branch block c.
Heart block occurs when electrical signals from the upper chambers of the heart atria cannot travel to the lower chambers ventricles. Normally the electrical signal that makes your heart beat travels from the top of your heart to the bottom. Right bundle branch block.
Second degree block is additionally divided into Mobitz type I and type II AV block. Usually the delay occurs in the AV node. First-degree AV block is rarely serious and may be left untreated in the vast majority of cases exceptions are discussed later.
A widened QRS complex is indicative of a diseased His-Purkinje system and the block location is usually infranodal 4 while a normal-width QRS andor a P-R interval greater than 300 ms are associated with nodal block. Which of the following best describes this pattern. First degree heart block is actually a delay rather than a block.
This can be due to an anatomical or functional impairment in the hearts conduction system. In some cases only occasional ventricular captures are observed and the dominant rhythm is maintained by a subsidiary pacemaker. TF Heart blocks are partial delays or complete interruptions in the cardiac conduction pathway between the atria and ventricles.

Second Degree Av Block Type 2 Acls Algorithms Com

Cardiac Muscle And Electrical Activity Anatomy And Physiology Ii

Conduction Disorders And Other Mi Complications Flashcards Quizlet
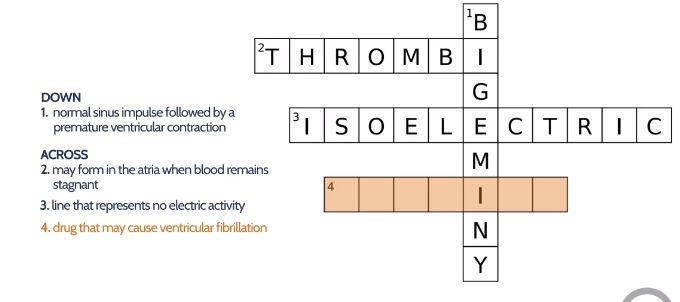
Electrocardiogram Flashcards Chegg Com
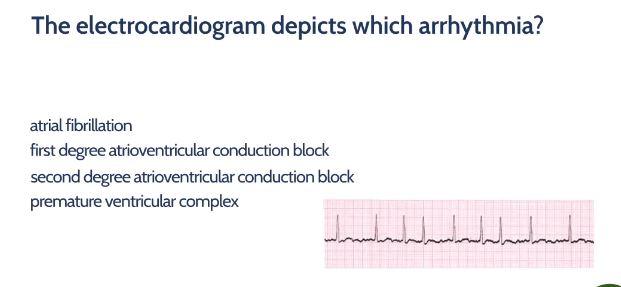
Electrocardiogram Flashcards Chegg Com
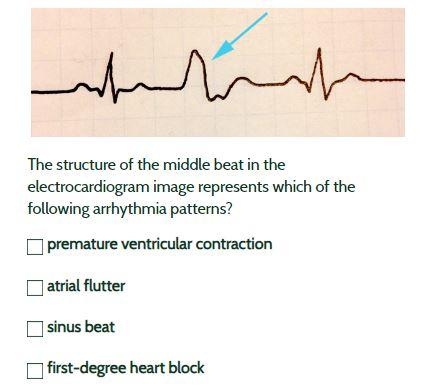
Electrocardiogram Flashcards Chegg Com

Fundamentalsofnursing Testbank2021
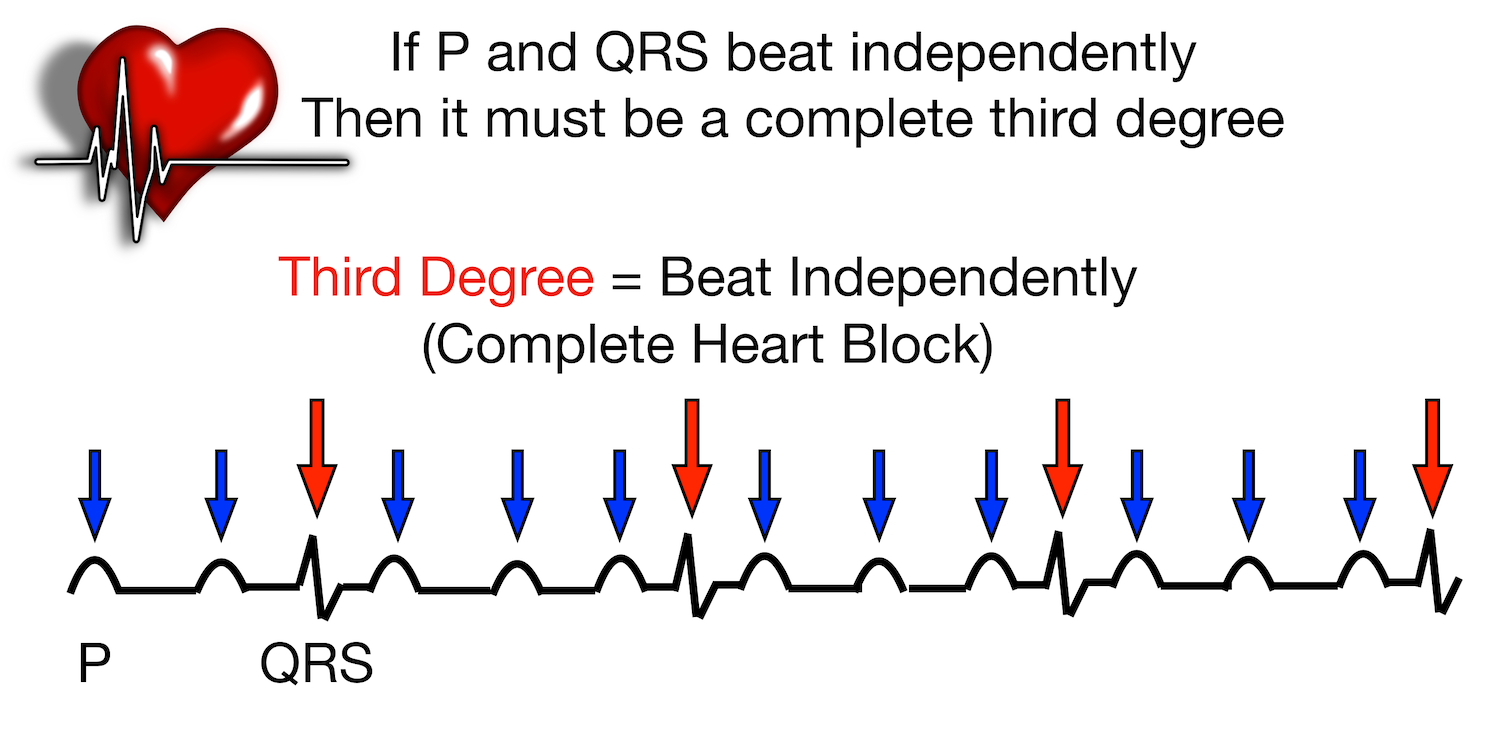
Av Heart Block Poem First Second Third Degree Types Ecg Rhythm Examples Explanation Made Easy Ezmed

Av Heart Block Poem First Second Third Degree Types Ecg Rhythm Examples Explanation Made Easy Ezmed

Cardiac Muscle And Electrical Activity Anatomy And Physiology Ii

First Degree Atrioventricular Block An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
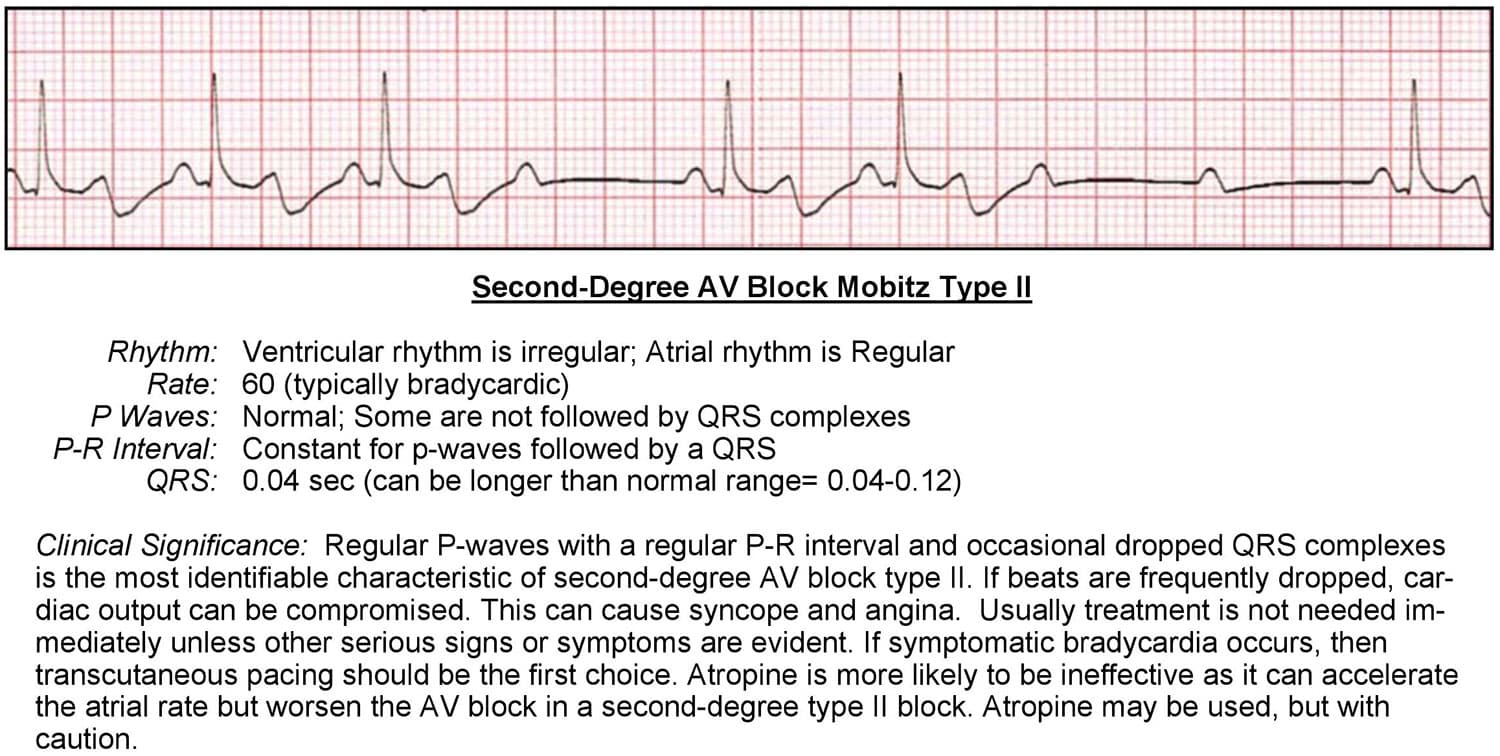
Atrioventricular Blocks Acls Wiki

Acls Final Review Flashcards Quizlet
Treatment For Atrioventricular Av Block In Washington Dc Maryland
Electrocardiogram Flashcards Chegg Com



Comments
Post a Comment